To view the animation, click here. Then click on the image to start the animation.
A) gametogenesis
B) sexual reproduction
C)meiosis
D) asexual reproduction
E) fertilization
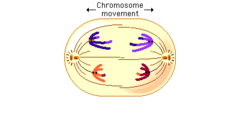
1) meiosis
2) fertilization
3) mitosis
4) the cell cycle
5) asexual reproduction
1) 23 pairs of
2) 5
3) 23
4) 46 pairs of
5) 46
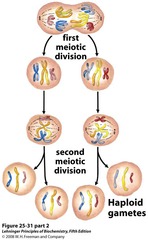
1) C and D
2) A and D
3) B and C
4) D
5) B
1) 16
2) 8
3) 64
4) 30
5) 32
four … diploid
two… diploid
two… identical to the other
four … haploid
two … haploid
four … identical to the other
four … haploid
two … haploid
two… diploid
four … diploid
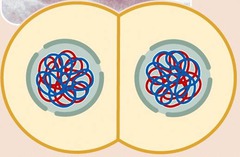
prophase I
telophase II and cytokinesis
anaphase II
prophase II
telophase I and cytokinesis
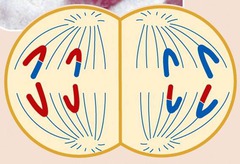
anaphase I
anaphase II
prophase II
interphase
telophase I and cytokinesis
telophase II and cytokinesis
telophase II
telophase I
telophase I and cytokinesis
telophase and cytokinesis
metaphase I
prophase I
prophase II
anaphase II
interphase
prophase II and cytokinesis
interphase
telophase I and cytokinesis
telophase II and cytokinesis
telophase and cytokinesis
telophase II
metaphase II
telophase I
telophase
interphase
metaphase II
metaphase I
telophase II and cytokinesis
prophase I
prophase II
anaphase I
interphase
anaphase II
prophase I
metaphase II
prophase II
metaphase I
metaphase II
telophase I and cytokinesis
anaphase I
metaphase II
anaphase II
prophase I
prophase II
telophase I and cytogenesis
metaphase II
anaphase I
metaphase I
telophase II and cytokinesis
prophase II
metaphase II
anaphase I
telophase I and cytokinesis
metaphase I
prophase I
metaphase II
telophase I and cytokinesis
prophase II
prophase I
anaphase I
prophase II
telophase II
prophase I
interphase
anaphase I
anaphase II
prophase II
telophase I and cytokinesis
prophase I
metaphase II
prophase II
prophase I
interphase
anaphase II
anaphase I
cytokinesis
random fertilization
crossing over
centromere separation
karyokinesis
B and C
D and E
A and B
A and D
A and C
two haploid cells.
four haploid cells.
eight haploid cells.
four diploid cells.
two diploid cells
anaphase I.
prophase I.
meiosis II.
metaphase I.
interphase.
the homologous chromosomes separate and move towards opposite poles.
homologous chromosomes stick together in pairs.
chromosome pairs are positioned in the middle of the cell.
there are four haploid daughter cells.
there are two daughter cells, each with 23 chromosomes.
prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, cytokinesis, meiosis II.
prophase I, anaphase I, metaphase I, telophase I, meiosis II, cytokinesis.
prophase I, anaphase I, telophase I, metaphase I, meiosis II.
metaphase I, prophase I, telophase I, anaphase I, cytokinesis, meiosis II.
metaphase I, prophase I, anaphase I, telophase I, cytokinesis, meiosis II.
telophase I.
anaphase I.
prophase I.
meiosis II.
Metaphase I.
mitosis … gamete formation
mitosis … meiosis
meiosis … fertilization
mitosis … fertilization
four diploid cells
four haploid cells
two diploid cells
two haploid cells
It provides eight haploid gametes and can eliminate chromosomes.
It allows genetic exchange and eliminates the formation of haploid cells.
It produces four haploid cells and allows exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes.
It provides for formation of four haploid cells and reduces the need for sister chromatids.
The sperm and egg have twice as many chromosomes as the parental cells.
Asexual reproduction requires the production of eggs and sperm.
Meiosis results in gametes that are used in reproduction.
Geneticists use the terms “son” and “daughter” to distinguish between cells resulting from cell division.
growth of a multicellular organism.
production of sperm and eggs.
cell replacement.
asexual reproduction.
produces a haploid individual
produces an individual with 23 chromosomes
allows a haploid sperm cell to fertilize a haploid egg cell
combines two diploid gametes, producing a zygote
Crossing over occurs.
Chromosomes move to the middle of the cell.
The number of chromosomes doubles.
Spindle formation occurs.
mitosis requires only one parent cell, but meiosis requires two parent cells
mitosis produces cells genetically identical to the parent cell, but meiosis does not
mitosis produces more daughter cells for each division than meiosis
mitosis produces haploid cells, but meiosis produces diploid cells
44 autosomes and two Y chromosomes
44 autosomes, one X chromosome, and one Y chromosome
22 autosomes and two Y chromosomes
46 autosomes, one X chromosome, and one Y chromosome
the nuclear envelope breaks up
crossing over occurs
sister chromatids separate and migrate to opposite poles
homologous chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell




