a. Right lateral
b. Left lateral
c. Right lateral decubitus
d. Left lateral decubitus
a. Inspiration
b. Full inspiration
c. Expiration
d. Prone
a. AP
b. PA
c. Oblique
d. Lateral
a. PA view
b. AP view
c. Lateral decubitus view
d. Oblique view
a. AP view
b. PA view
c. Apical view
d. Lateral decubitus view
a. AP view
b. PA view
c. Lateral decubitus view
d. Lateral view
a. Right lateral
b. Left lateral
c. Right lateral decubitus
d. Left lateral decubitus
a. Right side chest X-ray
b. Left side chest X-ray
c. Left lateral decubitus chest X-ray
d. Right lateral decubitus chest X-ray
a. Medulloblastoma
b. Ependymoma
c. Oligodendroglioma
d. Meningioma
a. Gestational sac
b. Fetal cardiac activity
c. Placenta
d. Fundal thickening
a. 2 hours
b. 4 hours
c. 6 hours
d. 8 hours
a. Radium 226
b. Bismuth 50
c. Iodine 131
d. Potassium 40
a. Bipedal lymphangiogram
b. Technetium 99m pyrophosphate scans
c. Restaging procedure
d. Gallium scan
a. Number of protons
b. Number of electrons
c. Number of neutrons
d. Electrons + Protons
a. Renal stones
b. Hypernephroma
c. Hydronephrosis
d. Polycystic kidney
a. Psedugout
b. Reiter’s syndrome
c. Hyperparathyroidism
d. Acromegaly
a. MRI
b. USG
c. CT scan
d. Plain X-ray
a. Open fontanelle
b. Inexpensive
c. Children more cooperative
d. Better resolution
a. Leukemia
b. Neuroblastoma
c. Bone secondaries
d. Multiple myeloma
a. Multiple myeloma
b. Kidney stones
c. Transplanted kidney
d. Renal cyst
a. Lateral view of Xray-chest
b. Echocardiography
c. USG
d. Cardiac catheterization
a. Echocardiography
b. Gallium scan
c. Angiography
d. USG
a. Ependymoma
b. Thrombosed cerebral veins
c. Sturge weber syndrome
d. Meningioma
a. Sturge-weber syndrome
b. Von-hippel lindau disease
c. Tuberous sclerosis
d. Neurofibroma
a. Iodine
b. Gadolinium
c. Rose Bengal
d. Strontium
Answer: All of them have egg shell calcificatoin
A helpful mnemonic for major causes of eggshell calcification in the thorax and mediastinum is:
A Silly Cool Sergeant Likes His Tubercular Blast
Mnemonic
A: amyloidosis
S: Silicosis
C: Coal workers’ pneumoconiosis (CWP)
S: Sarcoidosis
L: Lymphoma: (postirradiation Hodgkin disease)
H: Histoplasmosis (e.g. pulmonary histoplasmosis)
T: Tuberculosis
B: Blastomycosis (e.g. pulmonary blastomycosis)
a. Silicosis
b. Sarcoidosis
c. Tuberculosis
d. Histoplasmosis
a. Inverted 3 appearance
b. Cobra head sign
c. Craggy popcorn appearance
d. Thumb print appearance
a. Saw tooth appearance
b. Nose pipe appearance
c. Thumb printing
d. Cobble stone appearance
a. 2-3
b. 1.2
c. 5.7
d. 3.4
a. Neutrons
b. Alpha rays
c. Gamma rays
d. Beta rays
a. 2.6 years
b. 5.2 years
c. 270 days
d. 3200 years
a. Pelvic X-ray abdomen
b. CT
c. USG
d. Hypotonic duodenography
a. PTC
b. ERCP
c. CT scan
d. USG
a. Angiography
b. ERCP
c. CT scan
d. Ultrasound
a. Hyperparathyroidism
b. Scurvy
c. Hypoparathyroidism
d. Milkman’s pseudofracture
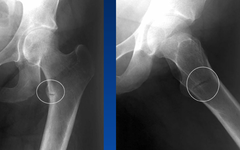
d. Osteomalacia
Milkman’s pseudofractures
– These lesions are composed of poorly mineralized osteoid matrix and are not true fractures or stress fractures.
– It appears as a thin, translucent band, about 2 mm in width, which runs perpendicular to the surface of the bone extending from the cortex inwards.
– They are oriented perpendicular to the long axis of the bone, and do not cross the entire bone.
– It represents insufficiency fractures through unmineralized osteoid in patients with osteomalacia.
– Common sites include axillary margins of the scapulae, ribs, pubic rami, proximal femurs, proximal ulnae and proximal humerus.
– Similar changes radiographically may be seen in Paget’s disease; however, they are only seen in involved bone and are not generalized.
In addition, the lines in Pagets occur on the convex side of the bone(tensile aspect) while in osteomalacia they occur on the concave side (compressive aspect).
The lines in Paget’s represent insufficiency fractures.
Read more:
1. http://www.mypacs.net/cases/OSTERMALACIA-WITH-LOOSERS-ZONES-805293.html
2. http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/arthritis-information/conditions/osteomalacia/symptoms.aspx
a. Vitamin C deficiency
b. Thyroiditis
c. Osteoporosis
d. Osteomalacia
a. M mode ECG
b. USG
c. Real time ECG
d. 2 D echocardiography
a. 10 days
b. 4 days
c. 8 days
d. 4 hours
a. 99m TC + 121 Gallium
b. 99m Tc DMSA
c. 99m Tc DTPA
d. 99m Tc DMSA
a. 20 rads
b. 10 rads
c. 5 rads
d. 1 rad
a. 5 mm Hg
b. 10 mmHg
c. 22 mm Hg
d. 40 mm Hg
a. Pulmonary edema
b. Mitral valve disease
c. Interstitial fibrosis
d. Bronchoalveolar carcinoma
a. Psychotic patients
b. Patients on lithium
c. Intracranial metallic aneurysm clips
d. Patients receiving radiotherapy
a. Plain X-ray
b. Fluoroscopy
c. MRI scan
d. CT scan
a. Ultraviolet rays
b. Beta rays
c. X-ray
d. Ultrasound
a. Angiography
b. CT scan
c. Enhanced MRI
d. MRI
a. EEG
b. Echoencephalography
c. Angiography
d. CT scan
a. Down syndrome
b. Sacral agenesis
c. Hydrocephalus
d. Anencephaly
a. AP view
b. Lateral view
c. Open mouth view
d. Dorsal view
a. I-131
b. Tc-99
c. Se-75
d. Cr-51
a. Splenic disease
b. Pulmonary embolism
c. Renal disease
d. Biliary tree
a. Ventilation perfusion scan
b. Contrast MRI
c. MRI
d. CT
a. Ventilation perfusion scan
b. Contrast MRI
c. MRI
d. CT
a. CT scan
b. Ventilation perfusion scan
c. USG
d. X-ray chest PA view
a. G2M stage
b. G2 stage
c. G1 stage
d. S phase
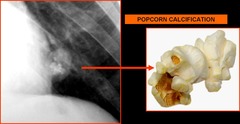
c. Hamartoma
Popcorn calcification:
– A cluster of sharply defined, irregularly lobulated, amorphous calcifications often with rings and arcs that resemble popped corn kernels.
– Usually seen in a pulmonary nodule
– Popcorn calcifications within a well circumscribed pulmonary nodule are highly suggestive of pulmonary chondroid hamartoma.
This type of calcification may be seen in many radiological settings including:
a. Chondroid lesions (e.g enchondroma, chondrosarcoma)
b. Fibrous dysplasia
c. Pulmonary hamartomas
d. Degenerating fibroadenomas of the breast
– They are also seen in metaphyses and epiphyses of long bones of children with osteogenesis imperfecta.
Read more:
1. http://posterng.netkey.at/esr/viewing/index.php?module=viewing_poster;task=viewsection;pi=121234;ti=406237;searchkey=
2. https://online.epocrates.com/u/2921547/Evaluation+of+solitary+pulmonary+nodule/Diagnosis/Approach
3. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/popcorn-calcification
a. Tuberculosis
b. Carcinoid
c. Hamartoma
d. Teratoma
a. Tuberculoma
b. Carcinoid
c. Hamartoma
d. Teratoma
a. Chest X-ray
b. Radionuclide lung scan
c. CT scan (HRCT)
d. Bronchography
a. USG
b. Bronchography
c. Bronchoscopy
d. X-ray
c. Driven snow appearance
Pindborg tumor:
Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor
On radiographs, it appears as a radiolucency (dark area) and is known for sometimes having small radiopacities (white areas) within it. In those instances, it is described as having a “driven-snow” appearance. Microscopically, there are deposits of amyloid-like material.
a. Sunray appearance
b. Onion peel appearance
c. Driven snow appearance
d. Cherry Blossom appearance
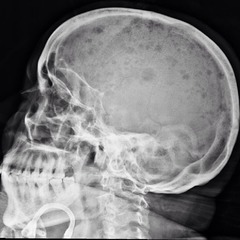
@ Punched out lucencies without surrounding osteosclerosis are the characteristic lesions seen on plain radiographs of the skull in the patient with disseminated myeloma.
In primary hyperparathyroidism, extensive resorption bone in the skull in combination with cystic areas of osteopenia are termed pepper pot skull.
1. http://images.md/myeloma-multiple-myeloma/
2. http://roentgenrayreader.blogspot.com/2012/09/pepper-pot-skull.html
a. Eosinophilic granuloma
b. Multiple myeloma
c. Craniopharyngioma
d. Paget’s disease
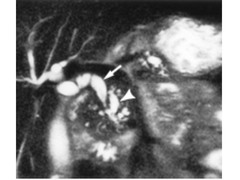
Dilatation of pancreatic side branches is more apparent on MRI than CT and may cause the so called “string of pearls” or “chain of lakes” appearance on MRCP.
See more at: http://www.appliedradiology.com/articles/imaging-of-the-pancreas-part-1#sthash.uqFPBiaZ.dpuf
a. Ductal adenoma
b. Carcinoma of head of pancreas
c. Acute pancreatitis
d. Osteopetrosis
a. Achondroplasia
b. Fluorosis
c. Osteogenesis imperfecta
d. Osteopetrosis
a. CT Scan
b. Oral cholecystography
c. USG
d. X-ray
a. Metastatic tumor of breast
b. Leiomyoma
c. Carcinoma lung
d. Malignant melanoma
a. Meningioma
b. Glioma
c. Craniopharyngioma
d. Medulloblastoma
a. INdium
b. Gallium
c. Technetium-147
d. Thallium-201
a. Electrical movement of nucleus
b. Magnetic movement of nucleus
c. Nuclear fission
d. Charge of nucleus
a. K+
b. N2O
c. H+
d. CO2
a. Electron
b. Neutron
c. Proton
d. Microwaves
a. Concentric dense calcification
b. Peripheral location
c. Cavitation
d. > 5cm in diameter
a. Neurofibroma
b. Hamartoma
c. Bronchial adenoma
d. Tuberculoma
a. 99m-Tc
b. 9-K
c. 201-Th
d. 60-Co
a. Iopanoic acid
b. Metrizamide
c Dianonosil
d. Conray (Iothalamate)
a. Platelet
b. Basophil
c. Lymphocyte
d. Neutrophil
a. Thallium technetium isotope substraction scan
b. Thallium scan
c. Gallium scan
d. CT scan
a. X-ray skull
b. MRI
c. Lumbar puncture
d. CT Scan
a. Streptomycin
b. Adriamycin
c. 5-FU
d. Mitomycin C
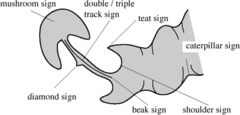
c. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
In HPS the pyloric channel appears “elongated”, because there is a failure in the relaxation of the pre-pyloric antrum.
Barium study is performed with the infant in the right anterior oblique position, to facilitate gastric emptying.
– Fluoroscopic observations include vigorous active peristalsis resembling a caterpillar and coming to an abrupt stop in the pyloric antrum, outlining the external thickened muscle as an extrinsic impression, termed the
@ Shoulder sign.
– The String Sign – appears when the channel is outlined by a string of contrast material
– The Double Track sign – appears when several linear tracts of contrast material are separated by the intervening mucosa.
– The Tit sign – appears when the luminal barium is transiently trapped between the peristaltic wave and the muscle.
USG signs:
1. The “cervix” sign: appearance of HPS on long-axis US images, resembling the uterine cervix.
2. The “donut” lesion : represents the sonolucent thickened muscle, located medial to the gallbladder and anterior to the kidney.
3. The “nipple” sign: The redundant mucosa may protrude into the distended portion of the antrum causing the nipple sign.
See more:
1.
http://posterng.netkey.at/esr/viewing/index.php?module=viewing_poster&task=viewsection&pi=126777&ti=433460&si=1482&searchkey=#poster
2.
http://posterng.netkey.at/esr/viewing/index.php?module=viewing_poster&task=viewsection&pi=5924&ti=31367&searchkey=
a. Irritable bowel syndrome
b. Ulcerative colitis
c. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
d. Toxic mega colon
a. Eosinophilic granuloma
b. Tuberculosis
c. Malignancy
d. Fracture of spine
a. Hypernephroma
b. Chronic pyelonephritis
c. Infantile polycystic kidney
d. Hydronephrosis
a. Rat tail configuration of vessels
b. Westermark’s sign
c. Normal X-ray
d. Pleural effusion
a. Cystitis
b. Ureterocele
c. Posterior urethral valve
d. Bladder tumor
a. Ventricular premature complex
b. WPW syndrome
c. Atrial fibrillation
d. Ventricular fibrillation
a. Radial artery
b. Axillary artery
c. Brachial artery
d. Femoral artery
a. Klinefelter syndrome
b. Marfan’s syndome
c. Down syndrome
d. Turner’s syndrome
a. Basal
b. A/P
c. Caldwell
d. Towne’s
a. 3.8 days
b. 4 days
c. 6 days
d. 5 days
a. Cesium
b. Uranium
c. Radon
d. Radium
a. Retinal detachment
b. Heating up of tissues
c. Microscopic hemorrhages
d. Convulsions
a. Ferromaggnetic
b. Piezoelectric
c. Ferro electric
d. Paramagnetic
a. Nitric oxide
b. Super oxide
c. Nitrous oxide
d. H2O2
a. Neutrons
b. Protons
c. Both a and b
d. Positrons
a. Branwald
b. Richard wolf
c. Edward Purcell
d. Goldman
a. Treatment by radiation
b. Use radium for diagnossi
c. Nucleic acid analysis
d. X-rays
a. Loudness
b. Intensity
c. Power
d. Frequency
a. 20/sec
b. 20-200/sec
c. 200/sec
d. More than 20,000/sec
a. Silicon
b. Lead zirconate titanate
c. Tungsten
d. Molybdenum
a. Californium
b. Polonium
c. Helium
d. Strontium
a. Radium
b. Strontium
c. Plutonium
d. Iridium
a. William harvey
b. Laennec
c. Lister
d. Robert Koch
a. Tachemig
b. Honarda
c. Coldmann
d. Helmholtz
Posterior iliac horn is seen in:
a. Marfan’s syndrome
b. Hurler’s syndrome
c. Ankylosing spondylitis
d. Nail patella syndrome
Chondrocalcinosis is seen in:
a. Rickets
b. Hypoparathyroidism
c. Ochronosis
d. Hyperthyroidism
Right heart border in a chest X-ray PA view is formed by all except:
a. IVC
b. SVC
c. Ascending aorta
d. Right atrium
In X-ray chest right border of mediastinum is formed by all except:
a. Right brachiocephalic vein
b. Right ventricle
c. Right atrium
d. Superior vena cava
In a chest X-ray, PA view, the right border of heart is not formed by:
a. Aorta
b. Superior vena cava
c. Right atrium
d. Inferior vena cava
For splenic rupture the investigation of choice is:
a. Peritoneal lavage
b. MRI
c. USG
d. CT
CT scan was invented by:
a. Godfrey Hounsfield
b. Eric Honda
c. John Snow
d. Suzuki Kobe
The first CT scanner was manufactured by:
a. Hitachi, Japan
b. Mitsubishi, Japan
c. Electro-musical instruments (EMI), England
d. General Electric, USA
Unit used in measuring the density of body tissues in CT scan is:
a. Hounsfield units
b. Ogawa units
c. Gray units
d. Mac units
Most radio dense substance is:
a. Bone
b. Soft tissue
c. Brain
d. Fluid
On usual CT scale of densities (-1000 to +1000), brain tissue measures:
a.-10 to +10
b. 0 to +20
c.+10 to +30
d. +22 to +46
X-rays are:
a. Neutrons
b. Electromagnetic waves
c. Electrons
d. Protons
Target material used for generating X-ray:
a. Tungsten
b. Cadmium
c. Cobalt
d. Palladium
X-ray with shorter wavelengths:
a. Are produced by lower KV
b. Have more penetrating power
c. Travel slower
d. Travel faster
X-rays are generated when …… strike tungsten:
a. Protons
b. Electrons
c. Electomagnetic waves
d. Neutrons
Time sector scanning of neonates is preferred because of which of the following practical reason:
a. Better resolution
b. Neonates are more cooperative
c. Inexpensive
d. Open fontanelle
Notching of ribs on X-ray is not seen in:
a. Aortitis
b. Neurofibromatosis
c. Coarctation of aorta
d. AV fistula
Rib notching is not seen in:
a. Neurofibromatosis
b. Hypoparathyroidism
c. Coarctation of aorta
d. Blalock-Taussig operation shunt
In coarctation of aorta the rib changes are seen from:
a. 1-12th
b. 3-6th
c. 8-12th
d. 4-9th
Not a radiological feature of mitral stenosis:
a. Kerley B-lines
b. Pulmonary hemosiderosis
c. Oligemia of upper lung field
d. Straight left heart border
“Ehrlenmeyer flask” appearance is seen in:
a. Thrombocytopenia
b. Sickel cell anemia
c. Chronic anemias
d. Gaucher’s disease
The amount of I¹³¹ used for a thyroid scan is:
a. 5 microcuries
b. 50 microcuries
c. 50 millicuries
d. 500 millicuries
The number of carpel bones seen in a radiograph of an infant is:
a. 0
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
isotope use in bone scans:
a. Technetium
b. Gallium
c. Selenium
d. Chromium
Beheaded Scottish terrier sign is seen in:
a. Spondylosis
b. Fracture rib
c. Spondylolisthesis
d. Fracture scaphoid
Scottish terrier sign is seen in:
a. AP view
b. PA view
c. Lateral view
d. Oblique view
Bronchorrhea is characteristically seen in:
a. Sarcoidosis
b. Scleroderma
c. Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma
d. Goodpasture’s syndrome
Renal papillary necrosis is associated with:
a. Sickel cell disease
b. Tuberculosis
c. Diabetes mellitus
d. All of the above
Neural tube defect is best detected by:
a. Placentography
b. Amniocentesis
c. Chromosomal analysis
d. USG
Water lily sign is found in:
a. Fungal granuloma
b. Actinomycosis
c. Hydatid cyst of liver
d. Hydatid cyst of lung
Phrygian cap is a feature of:
a. Stomach
b. Kidney
c. Gall bladder
d. Pancreas
Calcification of heart wall is suggestive of:
a. Endomyocardial fibrosis
b. Fibroelastosis
c. Carcinoid syndrome
d. Scleroderma
Thickness of stomach in USG is:
a. 10 mm
b. 7 mm
c. 5 mm
d. 2 mm
“Double bubble” sign on plain X-ray of abdomen is seen in:
a. Lleal atresia
b. Jejunal atresia
c. Duodenal atresia
d. Pyloric stenosis
For small intestine tumor the investigation of choice is:
a. CT scan with contrast
b. X-ray abdomen
c. Echocardiography
d. Barium meal swallow
Cardiac catherization was first attempted by:
a. Philip Bozzini
b. Gustav Killian
c. Dulius Bruck
d. Warner Forssmann
MOnge’s disease is seen in:
a. Lowlander’s in highland
b. Highlander in lowland
c. Highlander’s in highland
d. None
‘Champagne glass’ pelvis is seen in:
a. Congenital dislocation of hip
b. Down syndrome
c. Achondroplasia
d. Cretinism
Optical activity of organic substances is measured by:
a. Spectrometer
b. Polarimeter
c. Photometer
d. Multimeter
True regarding Hydatid cyst of lung in a chest X-ray:
a. Is seen on a Calcified ring shadow
b. shows spackled calcification
c. Calcification is rare
d. A and B are correct
Deleterious effect of ultrasound on small organism is:
a. Ionization
b. Vacuolation
c. Cavitation
d. Disintegration
Radioactivity was discovered by:
a. Marie Curie
b. Pierre Curie
c. Rutherford
d. Henri Becquerel
Radioactivity was discovered by Becquerel in:
a. 1796
b.1896
c. 1901
d. 1946
Basal ganglia calcification is seen in:
a. Hypoparathyroidism
b. Fahr’s syndrome
c. Mitochondria cytopathy
d. All of the above
Xeroradiography is used in…………cancer detection:
a. Stomach
b. Breast
c. Colonic
d. Pancreatic
Radiation protection shields are made up of:
a. Copper
b. Silver
c. Lead
d. Tin
Raised intracranial tension in adults is seen as:
a. Silver beaten appearance
b. Separation of sutures
c. Erosion of sella
d. All of the above
Onion peel appearance is seen in:
a. Osteoclastoma
b. Chrondosarcoma
c. Osteosarcoma
d. Ewing’s sarcoma
Stryker view is used in shoulder joint to visualize:
a. Recurrent subluxation
b. Subacromial calcification
c. Bicipital groove
d. Muscle calcification
Suprasellar calcification is seen in:
a. Craniopharyngioma
b. Meningioma
c. Calcified pineal gland
d. Pituitary adenoma
Radium emits:
a. Electrons
b. X-ray
c. Alpha rays
d. Gamma rays
Best diagnostic proceedure in acute pancreatitis is:
a. CT scan
b. MRI scan
c. Ultrasound scan
d. Pipida scan
Centenary year for X-ray is:
a. 1995
b. 1997
c. 1999
d. 2001
Medical thermography is based on the principle of man emitting:
a. X-ray
b. Ultrasonic rays
c. Ultraviolet radiation
d. Infrared radiation
which is the most common sign of subphrenic abscess:
a. Basal consolidation
b. Tented diaphragm
c. Pleural effusion
d. Subdiaphragmatic calcification
Best investigation for acute cholecystitis is:
a.Plain X-ray
b. PIPIDA scan
c. HIDA scan
d. Technetium scan
‘Figure of 3’ appearance is seen in:
a. Coarctation of aorta
b. TOF
c. TGV
d. All of the above
Thesaurosis is a disease said by some to be related to:
a. Molding of copper tube
b. Resins in hairspray
c. Inhalation of barium dust
d. In eosinophilia
“Reverse 3 sign” of Frostberg in barium study indicates:
a. Reversed midgut rotation
b. Periampullary atresia
c. annular pancreas
d. Duodenal atresia
a. Arteriography
b. MRI
c. USG
d. CT scan
A break in Shenton’s line is seen in:
a. Cretinism
b. Development displasia of hip
c. Down syndrome
d. All of the above
Echoencephalography is most useful for detecting:
a. Ventricular dilatation
b. Midline shift
c. Epilepsy
d. Vascular lesions
osteoporesis is diagnosed by all except:
a. Dual energy X-ray densitometry
b. Dual-photon absorptiometry
c. Plain X-ray
d. CT scan
String sign of Kantor is seen in:
a. Crohn’s disease
b. TB of the ileocaecal region
c. Idiopathic hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
d. All of the above
Signs of increased intracranial tension in a child in a skull X-ray:
a. Separation of sutures
b. Tense anterior fontanelle
c. Silver beaten appearance of bones
d. All of the above
“Lead pipe” appearance in barium enema is seen in:
a. Crohn’s disease
b. Ulcerative colitis
c. Schistosomiasis
d. Carcinoma colon
Intracranial calcification in skull X-ray may be seen in:
a. Pineal calcification
b. Cockayne’s syndrome
c. Cysticercosis
d. All of the above
Radioactive gold is used in:
a. Bladder
b. Malignant ascites
c. Glioma
d. None
Hot nodule is seen in:
a. Adenolymphoma
b. Mixed parotid
c. Adenocystic carcinoma
d. all of the above
Oligemic lung fields are seen in:
a. TOF
b. Pulmonary stenosis
c. ASD
d. Both A and B
Contrast material used in the diagnosis of esophageal atresia is:
a. Barium swallow
b. Gastrografin
c. Conray
d. Propyliodone (Dianosil)
Hair on end appearance in skull X-ray is characteristic of:
a. Sickle cell anemia
b. Megaloblastic anemia
c. Hemochromatosis
d. Thalassemia
Chest X-ray of a newborn with respiratory distress shows multiple air containing lesions in left hemithorax and mediastinal shift. Likely diagnosis is:
a. Pneumatocetes
b. Neonatal emphysema
c. Diaphragmatic hernia
d. Congenital lung cysts
Investigation of choice for spinal cord tumor is:
a. Myelography
b. CT scan
c. Plain X-ray
d. MRI
‘Doughnut’ sign seen on a brain scan usually suggests:
a. Osteoid osteoma
b. Metastases
c. Fibrous dysplasia
d. All of the above
The treatment of choice for anaplastic carcinoma thyroid is:
a. External radiation
b. Surgery
c. Radiotherapy
d. Thyroxin
Splenic calcification occurs in:
a. Tuberculosis
b. Malaria
c. Gaucher’s disease
d. Celiac disease
The photosensitive material used in X-ray films consists of:
a. zinc sulphate
b. Silver bromide
c. Cadmium bromide
d. Cellulose
In color doppler the color depends upon:
a. Strength of returning echo
b. Relation of transducer to blood flow
c. Frequency of doppler used
d. Type of Doppler machine used
When bones show a “bone within bone” appearance this is indicative of:
a. Chronic myelogenous leukemia
b. Bone infraction
c. Osteoporesis
d. Sickel cell anemia
Soft tissues calcification can be seen around the hip joint on a plain radiograph in all except:
a. Poliomyelitis
b. Melorheostosis
c. Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
d. Tumor calcinosis
Convolution markings in a child usually disappear by the age of…….
a. 3 months
b. 6 months
c. 3 years
d. 12 years
Regarding syringomyelia all are true except:
a. Is associated with Dandy- Walker malformation
b. Is commonly associated with Amlod-Chiari syndrome
c. Is associated with a scoliosis
d. Is associated with Klippel-Feil Syndrome
Massive splenomegaly is seen in the following conditions except:
a. Hairy cell leukemia
b. Sarcoidosis
c. Celiac disease
d. Polycythemia rubra vera
which of the following is false regarding ” j shaped sella”
a. Normal varient in 30% of cases
b. Seen in optic glioma
c. Associated with Hurler’s syndrome
d. Associated with low grade hydrocephalus
“Sunray” appearance on X-ray is seen in:
a. Ewing’s sarcoma
b. Osteogenic sarcoma
c. Osteomyelitis
d. Chondrosarcoma
Most common site of spinal bifida is:
a. Cervical
b. Lumbosacral
c. Sacral
d. Dorsal
Pantomography is done for all except:
a. TM joint
b. Dental cyst
c. Dental caries
d. Transverse fracture of atlas
Most common cause of spontaneous pneumothorax:
a. Tuberculosis
b. Bronchogenic carcinoma
c. Rupture of sub-pleural blebs
d. Bronchial adenoma
Hydrocephalus in children, first seen is:
a. Sutural diastasis
b. Sellar erosion
c. Large head
d. Thinned out vault
Seldinger needle is used for:
a. Arteriography
b. Ureterography
c. Arthrography
d. Sonography
Epiphyseal dysgenesis is a pathognomonic feature of:
a. Hyperthyroidism
b. Hyperparathyroidism
c. Hypothyroidism
d. Hypoparathyroidism
All are associated with greenhouse effect except:
a. CO?
b. N?
c. CH?
d. O?
“Round pneumonia” occurs in:
a. Children
b. Adult males
c. Adult females
d. Elderly
Stenver’s view is used to visualize:
a. Temporomandibular joint
b. Optic foramina
c. Mastoid air cells
d. Internal auditory meatus
Cavitating lesions in lung are found in:
a. Squamous cell carcinoma
b. Adenocarcinoma
c. Small cell carcinoma
d. Large cell carcinoma
In urinary schistosomiasis , calcification is commonly seen in:
a. Bladder
b. Entire ureter
c. Lower half of the ureters
d. Upper half of the ureters
Most common cause of intracranial calcification is:
a. Pineal calcification
b. Intracranial aneurysm
c. Meningioma
d. Tuberculoma
Calcification and sclerosis of the fibrous cardiac skeleton is suggestive of:
a. Lev’s disease
b. Lenegre’s disease
c. Both
d. None
A neonatal presents with history of having passing meconium. On examination there is no anal opening. Investigation of choice is:
a. Invertogram
b. Gastrograffin study
c. X-ray erect posture
d. X-ray supine posture
Curie is the unit for:
a. Radiation emitted
b. Radiation absorbed
c. Radioactivity
d. None of the above
Most important investigation for posterior urethral valve is:
a. Micturating cystogram
b. Retrograde cystogram
c. IVP
d. Plain X-ray
Dye used for bronchography is:
a. Iopanoic acid
b. Sodium diazotize
c. Meglumine lothalamate
d. Propyliodone (Dianosil)
The substance used for oral cholecystography is:
a. Iopanoic acid
b. Sodium diazotize
c. Meglumine iothalamate
d. Dianosil
Contrast used in liver scan is:
a. TechneColl (tecnetium ??m)
b. I¹³¹ Rose Bengal
c. Gallium²³?
d. Thallium ²?¹
Dye used in intravenous cholangiography is:
a. Dianosil
b. Conray
c. Cholografin
d. Myodil
While doing renal scan, hippuran (orthoiodohippurate) is attached to:
a. Iodine¹²?
b. Iodine¹³¹
c. Iodine¹³²
d. Iodine¹¹³
“Target sign” in CT scan means:
a. Ovarian carcinoma
b. Ectopic kidney
c. Intussusception
d. Liver metastasis
Lymphangiomyomatosis is characterized by all of the following except:
a. Postmenopausal women
b. Recurrent chylous pleural effusions
c. Miliary densities
d. Recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax
In colitis cystica profunda:
a. Cysts may be up to 2 cm in diameter
b. On a barium enema the appearance is indistinguishable from adenomatous polyps
c. Benign condition
d. All of the above
An aneurysm of the sinus of valsalva usually ruptures into:
a. Right atrium
b. Left atrium
c. Posterior aortic sinus
d. Left ventricle
Pneumomediastinum can be seen in:
a. Valsalva maneuver
b. Ketoacidosis
c. Asthma
d. All of the above
Unit of one dose of radiation absorbed is:
a. Gray
b. Roentgen
c. Curie
d. Becquerel
In aortic dissection the investigation of choice is:
a. ECG
b. Aortagraphy
c. CT scan
d. MRI scan
Estimation of fetal maturity by biparietal sonic measurement at 20-28 weeks of gestation is accurate to within +/-:
a. & days
b. 14 days
c. 10 days
d. 20 days
Investigation of choice for acute subarachnoid hemorrhage:
a. Enhanced MRI
b. MRI
c. CT scan
d. Angiography
Diagnostic of rickets on X-ray is:
a. White line of Frankel
b. Epiphyseal widening
c. Periosteal elevation
d. Cupping and flaring
A characteristic of benign tumor of lung in X-ray is:
a. Size >5 cm diameter
b. Peripheral location
c. Cavitation
d. Calcification
The following is a radiolucent renal stone:
a. Cystine
b. Calcium phosphate
c. Uric acid
d. Calcium oxalate
Fish mouth vertebra occurs in the:
a. Osteogenesis imperfecta
b. Ehler-Danlos syndrome
c. Gaucher’s disease
d. Marfan’s syndrome
Coffee bean sign indicates:
a. Toxic megacolon
b. Volvulus of cecum
c. Strangulation of incompletely odstructed loop of small bowel
d. Mesenteric artery embolism
Chickenpox pneumonia is characterized by:
a. Nodular infiltrate
b. Basilar infiltrate
c. Pulmonary edema
d. Linear pattern
Candle wax appearance is seen in:
a. Osteogenesis imperfecta
b. Meloorheostosis
c. Diaphyseal dysplasia
d. Exoxtosis
Primary anomaly in Klippel-Fell syndrome is:
a. Torticolitis
b. Fusion
c. Absence
d. Segmentation
Loss of lamina dura is observed in:
a. Cushing’s disease
b. Legg-Calve-Perthe’s disease
c. Hyperparathyroidism
d. Osteoporesis
Hamman-Rich syndrome is:
a. Fibrosing alveolitis
b. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
c. Recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax
d. Central mediastinal adenopathy
Batwing pattern of pulmonary edema is typical of:
a. Renal failure
b. CCF
c. ILD
d. Sarcoidosis
Differential diagnosis of honeycomb lung includes:
a. Eosinophilic granuloma
b. Sarcoidosis
c. Both
d. None
Pancoast tumor is most commonly due to which cell type:
a. Squamous
b. Columnar
c. Adenocarcinoma
d. pseudo-stratified
Ulcer crater on barium X-ray examination indicates the diagnosis of :
a. Gastric carcinoma
b. Duodenal ulcer
c. Duodenal diverticulum
d. Duodenal stricture
Best diagnostic modality for subphrenic abscess is:
a. Plain X-ray
b. Ultrasound
c. CT scan
d. Diagnostic laparotomy
Lateral source of neutrons for radiotherapy is:
a. Strontium 90
b. Iodine 131
c. Californium 252
d. Radium 226
Terminal phalangeal sclerosis is associated with:
a. Rheumatoid arthritis
b. Normal variation
c. Sarcoidosis
d. All of the above
Round, smooth, slightly lobulated peripheral opacity in the lung with calcification is a feature of:
a. Hamartoma
b. Hydatid cyst
c. Amoebic abscess
d. Carcinoma lung
Wimberger,s ring is seen in:
a. Scurvy
b. Rickets
c. Osteomalacia
d. Osteoporesis
Brachytherapy means:
a. Irradaiation by radiopharmaceuticals
b. Irradiation of tissue at 3 cm from the surface
c. Irradiation of tissue by placing radioactive sources into the tissue
d. Irradiation of tissue from a distance
Type of radiation used in radiotherapy is:
a. Photons
b. Infrared rays
c. Ionizing radiation
d. UV rays
Which of the following is provided by linear accelerator:
a. Infrared rays
b. Neutrons
c. Electrons
d. Protons
Atomic weight is equal to the number of:
a. Neutrons
b. Protons and neutrons
c. Electrons
d. Protons
Normal metacarpel index is:
a. >10.4
b. >5.4
c. 5.4-7.9
d. 8.4-10.4
Tear drop sign is seen in:
a. Posterior cranial fossa
b. Maxillary sinus
c. Zygoma fracture
d. Blow-out fracture of orbit
Which of the following is differential diagnosis for miliary shadow in chet X-ray:
a. Tuberculosis
b. Pulmonary siderosis
c. Histoplasmosis
d. All of the above
Figure of “8” features are seen in which of the following:
a. TOF
b. Abnormal origin of aorta
c. TAPVC
d. Partial APVC
Best conductor of electricity is:
a. Diamond
b. Coke
c. Coal
d. Graphite
Which of the following is a characteristic radiological finding in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis:
a. Gas in the portal system
b. Gas in the intestinal wall
c. Pneumopritoneum
d. Air fluid levels
In the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma one of the following radionuclide scan is useful:
a. MIBG scan
b. MIDA scan
c. DTPA scan
d. DMSA scan
Radiological investigation in female of reproductive age should be restricted to:
a. First 10 days of menstrual cycle
b. Period of menstruation
c. 10-20th day of the cycle
d. Last 10 days of the cycle
Percentage of cold thyroid nodule likely to be malignant is:
a. 72%
b. 20%
c. 40%
d. 30%
The test , which is both sensitive and specific for diagnosis of renal artery hypertension is:
a. Captopril-enhanced radionucleotide renal scan
b. Angiography
c. CT
d. MRI
Stereotactic radiosurgery is a form of:
a. Radiotherapy
b. Radio-iodine therapy
c. Robotic surgery
d. Cryosurgery
Which one of the following radioisotope is commonly used as a source for external beam radiotherapy in the treatment of cancer patients?
a. Strontium-89
b. Radium-226
c. Cobalt-59
d. Cobalt-60
“Bracket” calcification of skull in X-ray is seen in:
a. Meningioma
b. Sturge-Weber syndrome
c. Corpus callosum lipoma
d. Tuberous sclerosis
A male patient presents with abdominal pain and distention. On barium enema examination, there is a “bird’s beak” deformity. Which of the following is the likely diagnosis?
a. Intussusception
b. Volvulus of the sigmoid colon
c. Enteric perforation
d. Crohn’s disease
Thickness of lead apron to prevent radiation is:
a. 0.5 mm
b. 7 mm
c. 3 mm
d. 1 mm
A young patient presents with history of dysphasia more to liquids than solids. The first investigation you will do is:
a. Barium swallow
b. Esophagoscopy
c. Ultrasound of the chest
d. CT scan of the chest
Fraying and cupping of metaphyses of long bones in an child does not occur in:
a. Rickets
b. Lead poisoning
c. Metaphyseal dysplasia
d. Hypophosphatasia
High resolution computed tomography of the chest is the ideal modality for evaluating:
a. Pleural effusion
b. Interstitial lung disease
c. Lung mass
d. Mediastinal adenopathy
Extensive pleural thickening and calcification especially involving the diaphragmatic pleura are classical features of:
a. Coal worker’s pneumoconiosis
b. Asbestosis
c. Silicosis
d. siderosis
Modality of choice for detection of acute subarachnoid hemorrhage is:
a. MRI
b. X-ray computed tomography
c. USG
d. Plain X-ray of skull
A 40 year old man presented with acute episode of GI bleeding. Initial management was given for 6 hours. Which is important procedure for diagnosis is:
a. Radiolabeled RBC
b. Barium meal
c. Endoscopy
d. USG
A patient has ARF but normal USG report. Next most useful investigation is:
a. DTPA scan
b. IV pyelography
c. Retrograde pyelography
d. Renal angiography
Which of the following isotopes is used to assess renal function?
a. DTPA
b. DMSA
c. Gallium
d. Thallium
Impaired renal function is assessed by:
a. MAGS
b. Iodihippurate
c. DMSA scan
d. DTPA
A patient has renal call carcinoma with thrombus in IVC and renal vein. Best investigation for diagnosis is:
a. IVP
b. Color Doppler imaging
c. CT scan
d. Angiography
A young girl presented with pain in chest. Pain is not associated with exercise. On auscultation there was multiple non-ejection clicks with murmur. Most important investigation for diagnosis is:
a. ECG
b. Tc pyrophosphate scan
c. Thallium scan
d. EEG
A 50 year old man who is a chronic smoker presents with single lymph node enlargement and hoarseness of voice. Next investigation should be:
a. FNAC
b. IDL with chest X-ray
c. Percutaneous biopsy
d. Advise him to stop smoking
In aortic dissection the investigation of choice is:
a. Digital segmental angiography
b. MRI
c. CT scan
d. USG
At birth first paranasal sinus to develop is:
a. Sphenoid
b. Frontal
c. Maxillary
d. Ethmoidal
An8 year old boy presents with back pain and mild fever. His plain X-ray of the dorsolumbar vertebra with preserved disc spaces. There was no associated soft tissue shadow. The most likely diagnosis is:
a. Ewing’s sarcoma
b. Tuberculosis
c. HIstocytosis
d. Metastasis
Which one of the following is a recognized X-ray feature of rheumatoid arthritis?
a. Juxta-articular osteosclerosis
b. Sacroilitis
c. Bone erosions
d. Peri-articular calcification
All of the following are X-ray features of rheumatoid arthritis except:
a. Soft tissue swelling
b. Osteoporosis
c. Periosteal new bone formation
d. Bony erosions
Which of the following is the best choice to radiological evaluation of a posterior fossa tumor?
a. CT scan
b. MRI
c. Angiography
d. Myelography
Treatment of carcinoma thyroid using radioactive iodine is:
a. I¹³¹
b. I¹²?
c. I¹³³
d. I¹??
Most suitable radioisotope of iodine for treating hyperthyroidism is:
a. I¹²³
b. I¹²?
c. I¹³¹
d. I¹³²
Radioiodine is not used in the treatment of which of the following:
a. Anaplastic carcinoma
b. Follicular carcinoma
c. Medullary carcinoma
d. Papillary carcinoma
Non-caseating granulomas are seen in all the following except:
a. Tuberculosis
b. Byssinosis
c. Hodgkin’s lymphoma
d. Metastatic carcinoma of lung
Pleural involvement in sarcoidosis is:
a. Unilateral
b. Bilateral
c. Very common
d. Very rare
X-rays are produced when:
a. Electron beam strikes the nucleus of the atom
b.Electron beam strikes the anode
c. Electron beam reacts with the electromagnetic field
d. Electron beam strikes the cathode
For the treatment of deep-seated tumors, the following rays are used:
a. X-rays and gamma rays
b. Alpha rays and beta rays
c. Electrons and prositrons
d. High power laser beam
Ionization radiation act on tissue depending upon:
a. Thermal injury
b. Formation at pyrimidine dimmers
c. Excitation of electron from orbit
d. Linear acceleration energy
Principle used in radiotherapy is:
a. Low dose causes tissue necrosis
b. DNA damage
c. Ionizing the molecule
d. Cytoplasmic coagulation
The maximum penetration among the following is seen with which ray:
a. Alpha
b. Beta
c. Gamma
d. Electron beam
Which of the following has the maximum penetrating power?
a. Alpha rays
b. Beta rays
c. Gamma rays
d. Electron beam
Characteristic finding in CT-scan of a TBM case is:
a. Exudates seen in basal cistem
b. Hydrocephalus is commonly seen
c. Ventriculitis
d. Calcification of cerebellum
What is the diagnostic radiological finding in skeleton fluorosis?
a. Sclerosis of sacroiliac joint
b. Interosseous membrane ossification
c. Osteosclerosis of vertebral body
d. Ossification of ligaments of knee joint
On CT-scan, all are seen as hypodense area except:
a. Cerebral hemorrhage
b. Glioblastoma
c. Cerebral edema
d. Cerebral infract
Pneumoperitoneum can be used to visualize peritoneal/retroperitoneal structures. The gas that is best for use in pneumoperitoneum is?
a. Oxygen
b. Nitrogen
c. CO?
d. N?O
Investigation of choice to demonstrate vesicoureteral reflex is:
a. Cystoscopy
b. IVP
c. Contrast MCU
d. Isotope cystogram
Radiation therapy is given to a carcinoma patient. After 2 days the most common skin manifestation is:
a. Dermatitis
b. Hyperpigmentation
c. Atopy
d. Erythema
Earliest skin change noticed after irradiation is:
a. Erythema
b. Hyperpigmentation
c. Ulceration
d. Dryness
Most common presentation of radiation carditis is:
a. Pyogenic pericarditis
b. Myocardial fibrosis
c. Atheromatous plaques
d. Pericardial effusion
Best diagnostic test for deep vein thrombosis is:
a. MRI
b. Venography
c. Impendence phlebography
d. Duplex USG
X-ray chest with reticular pattern, air bronchogram sign is seen in:
a. Septicemia
b. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
c. Pulmonary hypertension
d. Respiratory distress syndrome
Intracavitary radiation is given in:
a. Oral cavity carcinoma
b. Esophageal carcinoma
c. Lung carcinoma
d. Cervix carcinoma
On X-ray all the following renal calculi can be seen except:
a. Calcium oxalate
b. Triple phosphate
c. Uric acid
d. Cystine stones
In bone-scan, hot spots are seen in all the following except:
a. Osteoblastic metastasis
b. Multiple myeloma
c. Osteomyelitis
d. Bony lesions of hyperthyroidism
In a patient with solitary nodule of thyroid, investigation of choice is:
a. FNAC
b. USG
c. CT
d. Radioisotope scan
Which of the following is the most radiosensitive phase of cell cycle?
a. G?
b. S
c. G?
d. M
MRI rooms are shielded completely by a continuous sheet or wire mesh of copper or aluminium to shield the image from external electromagnetic radiations, etc., it is called:
a. Maxwell cage
b. Faraday cage
c. Edison’s cage
d. Ohm’s cage
A 45 year old coal mine worker presents with:
a. Sjogren’s syndrome
b. Caplan’s syndrome
c. Silicosis
d. Wegeneer’s granulomatosis
A patient is suspected to have vestibular schwannoma, the investigation of choice for its diagnosis is:
a. Contrast enhanced CT scan
b. PET Scan
c. SPECT
d. Gadolinium enhanced MRI
In which of the folowing, a Coer-en-Sabot’ shape of the heart is seen?
a. Tricuspid atresia
b. Tetralogy of fallot
c. Transposition of great arteries
d. VSD
In scurvy all of the following radiological signs are seen except:
a. Zone of demarcation near epicnysis
b. Soap bubble appearance
c. Frenkel’s line
d. Pelican spur
A 50 year old smoker male presents with pain along the left arm and ptosis:
a. Adenocarcinoma lung
b. Bronchial carcinoid
c. Pancoast’s tumor
d. Bronchoalveolar carcinoma
Sunray appearance on X-ray is suggestive of:
a. A chondrosarcoma
b. A metastatic tumor in the bone
c. An osteogenic sarcoma
d. An Ewing’s sarcoma
The investigation of choice for imaging of urinary tract tuberculosis is:
a. Plain X-ray
b. IV urography
c. USG
d. CT
Which of the following technique uses piezoelectric crystals?
a. USG
b. NMR imaging
c. X-ray diffraction
d. Xeroradiography
In which of the following conditions the lead pipe appearance of the colon on a barium enema is seen?
a. Amebiasis
b. Ulcerative colitis
c. Tuberculosis of colon
d. Crohn’s involvement of the colon
The EEG cabins should be completely shielded by a continuous sheet of wire mesh of copper to avoid the picking up of noise from external electromagnetic disturbances. Such a shielding is called as:
a. Maxwell cage
b. Faraday cage
c. Edison’s cage
d. Ohm’s cage
The technique employed in radiotherapy to counteract the effect of tumor motion due to breathing is known as:
a. Arc technique
b. Modulation
c. Gating
d. Shunting
Gamma camera in ‘Nuclear medicine’ is used for:
a. Organ imaging
b. Measuring the radioactivity
c. Monitoring the surface contamination
d. RIA
In which one of the following conditions, the sialography is contraindicated:
a. Ductal calculus
b. Chronic parotitis
c. Acute parotitis
d. Recurrent sialadenitis
Which of the following ultrasound marker is associated with greatest increased risk for trisomy 21 in fetus?
a. Echogenic foci in heat
b. Hyperechogenic bowel
c. Choroid plexus cysts
d. Nuchal edema
In CT, the attenuation values are measured in Hounsfield units (HU). An attenuation value of ‘0’(zero) HU corresponds to:
a. Water
b. Air
c. Very dense bone structures
d. Fat
The most sensitive imaging modality for diagnosing ureteric stones in a patient with acute colic is:
a. X-ray KUB region
b. Ultrasonogram
c. Non contrast CT scan of the abdomen
d. Contrast enhanced CT scan of the abdomen
Which of the following is the investigation of choice for assessment of depth of penetration and perirectal nodes in rectal cancer?
a. Transrectal USG
b. CT scan of pelvis
c. MRI
d. Double contrast barium enema




