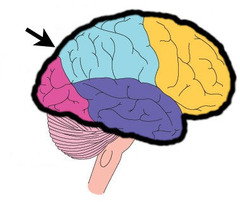
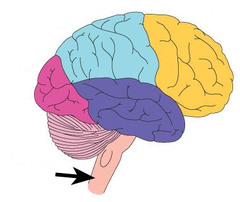
neurons communicate with each other every single second, that’s how it tell you to be careful not to fall or light on your eyes, to close them
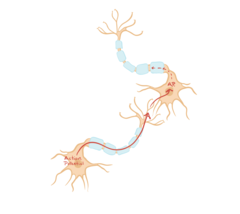
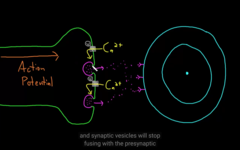
Action potential travels down an axon
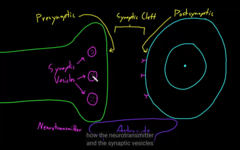
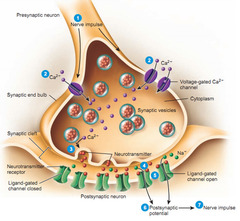
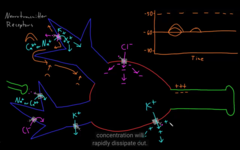
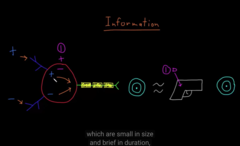
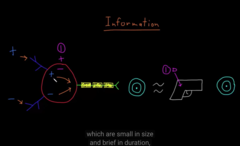
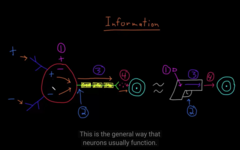
The space between the pre- and post synaptic cleft are called ” SYNAPSE” You can also find NT in there
glutamate: excitatory (Na+)
gaba: inhibitory (Cl-)
dopamin, histamin (allergies), serotonin, and adrenaline ( stress)
what are some NT?
axon terminal contacting the cell, gap contained, it released molecules at the synapse that passes to the membrane of the target cells
Chemical synapse has a gap
the cells are physically connected, they are connected to the cell membrane. the axon terminal specifically bind the target cells: Inside of neuron talks with the inside of the cell. Cytoplasm of the two connected. ions directly connected.
Electrical synapse has no gap
chemical synapse
The most common form of the synapse in human would be the
pre synaptic vs. post synaptic
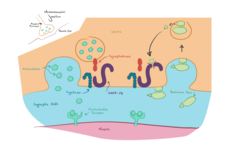
when calcium enters from the outside, this cause the membrane to diffuse with the and exit all of the NT that it contains:
NT are molecules that communicate information between neuron and it’s target cells. There are 100’s of neurotransmitters
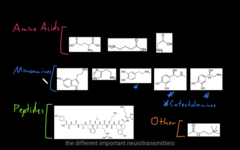
Types of NT
amino group and carboxylic group, peptide NT’s. Peptides are chains of amino acids, bunch of them together and we called them peptides.
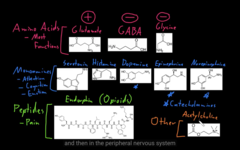
* glutamate (+), GABA (-), Glycine
NT amino acids
these are biogenetic amines, mono amines are organic molecules, connected to an aromatic group and the amino group connected by carbon chains. catecarlamines, (sub group of amino, which has a benzene, had hydroxy amine)
* serotonin, histamine, (dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine: catecholamine)
conciseness, cognition, thinking, emotions,
many disorder has to do with monoamines! (Opioids: endorphine, has to do with pain receptors.
NT monoamines
ACTH: central nervous system, peripheral NS, motor neurons synapse at the skeletal muscles.
other molecular NT:
Amino acids, monoamines, peptides and other NT’s.
Dendrites: excitatory
Cell body: inhibitory
terminal: excitatory/ inhibitory
NT could be excitatory or inhibitory:
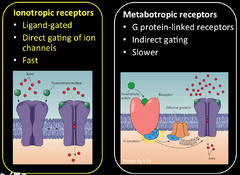
metabotropic vs. inotropic
inotropic, ligand gated ion channel : Cl-, Ca++, Na+, K+ –> depolarization
metabotropic: secondary messenger neuron
-change the activity of protein + genes
-affect is larger!
The interaction of metabotropic vs. inotropic
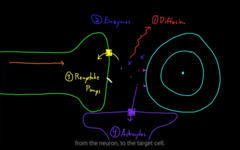
1) Diffusion, slowing up the action potential
2) Enzymes: synapse break down the NT into compartments
3) Re-uptake pump, actively removes the NT from the synapse
4) Astrocytes: CNS, absorbs NT inside
ALL this TURNs it ON/ OFF
How to remove NT from a synapse
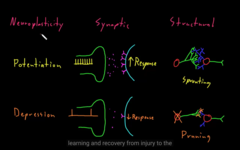
How the nervous system changes in response to experiance
Neuroplasticity
changes in synapses and other parts of the neuron
Neuroplasticity
potentiation, parts mostly used
strength of information can increases and it is called
depression, parts used rarely
strength of information can decrease and it is called
when it happens at the level of synapse, or at level of enter cell: structural
synaptic Neuroplasticity
Look at it careful, it is used most of often today…
potentiation vs. depression Neuroplasticity
C
Which term describes the space between a neuron and its target cell?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Axon terminal
Post synaptic membrane
Synaptic cleft
Dendritic spine
Both chemical and electrical synapses relay information through similar mechanisms.
Which of the following statements does not accurately describe synapses?
Voltage-gated calcium channels
What channel plays a role in the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft?
Action potentials ultimately result in more calcium leaving the target cell at the post synaptic membrane.
Which of the following statements about action potentials and information transmission in the synaptic cleft is false?
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
What is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain?
Histamine
Which neurotransmitter is not classified as a catecholamine?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
Histamine
Dopamine
Metabotropic neurotransmitter receptors move more slowly than ionotropic neurotransmitter receptors.
There are two main types of neurotransmitter receptors. Which of the following statements about receptors accurately describes how they function?
Enzymatic deactivation
How is acetylcholine removed from the postsynaptic membrane?
Structural depression
Which of the following terms describes the type of plasticity that occurs when entire neurons are lost due to decreased activity?
Serotonin
One specific type of antidepressant medication works by blocking the removal of neurotransmitters. Which of the following neurotransmitters is most likely the target of the antidepressant medication?
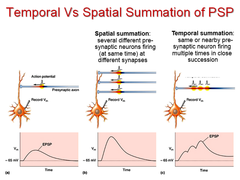
temporal vs. spatial summation
Everything about summation
everything about summation
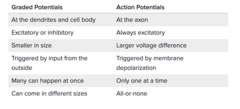
Graded potential vs. Action Potential
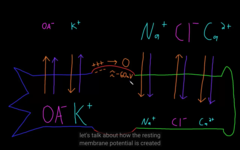
The neuron resting potential maintain -60 mV
The outside: negative
The inside: positive
The electrical: each membrane attracted to the OPP charge
The chemical force: The concentration gradient, diffusion force.
Electrical vs. chemical gradient
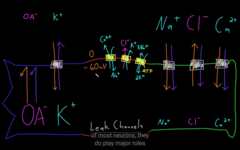
Look how the ions gets in in out of the cell:
How neurons created and why they decay over time
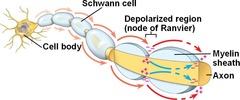
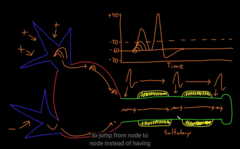
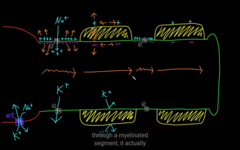
jumps from node to node
Saltatory conduction
How the action potential takes place across an axon
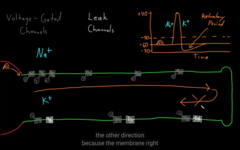
because the membrane is in refractory period.
AP goes only in one direction, why?
Learn how action potential working and, leak channels and voltage gated.
it makes it faster
less resistance
more conduction
more ions flow and inc A.P
How does myelination changes action potential?
larger vs. smaller axon
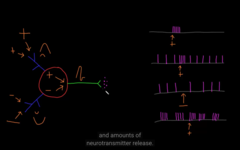
Action Potential Patterns: temporal response pattern amount of NT release.
D
Which of the following is the correct definition of a cation?
Please choose from one of the following options.
A cation is a negatively charged ion.
A cation is an ion that can have a positive or negative charge.
A cation is an ion that cannot have a charge.
A cation is a positively charged ion.
A
Which term describes the cell membrane potential of a neuron at rest?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Polarized
Hyperpolarized
Repolarized
Depolarized
B
How are potassium ions typically moved out of a neuron when the membrane is at rest?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Electrical gradients move potassium ions out of the cell.
Concentration gradients move potassium ions out of the cell.
Potassium ions are stable and do not move when a membrane is at rest.
The sodium-potassium pump moves potassium ions out of the cell.
A
Action potentials are characterized by which of the following?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Rapid depolarization
Repolarization
Slightly negative polarization
Depolarization or hyperpolarization
C
Absolute and relative refractory periods are important aspects of which of the following?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Graded potentials
Equilibrium potentials
Action potentials
Resting potentials
B
Which of the following statements is false?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Refractory periods are not associated with graded potentials, but are associated with action potentials.
Graded potentials are always hyperpolarizing, whereas action potentials are always depolarizing.
Graded potentials are always decremental, whereas action potentials are always non-decremental.
Graded potentials are proportional to the magnitude of the stimulus, whereas action potentials are “all-or-none.”
B
Which statement describes the membrane potential at the peak of an action potential?
Please choose from one of the following options.
The membrane potential is much more positive than the Na+ equilibrium potential.
The membrane potential is slightly less positive than the Na+ equilibrium potential.
The membrane potential is slightly more positive than the Na+ equilibrium potential.
The membrane potential is the same as the Na+ equilibrium potential.
C
How would action potentials be affected in a myelinated axon if nodes are far apart?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Action potentials would not be affected
Action potentials might travel more slowly
Action potentials might stop
Action potentials might travel more quickly
C
Which of the following neuronal processes transmits an action potential?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Dendrite
Soma
Axon
Glia
C
Saltatory conduction refers to which of the following?
Please choose from one of the following options.
The conduction of a graded potential along a demyelinated axon.
The conduction of a graded potential along a myelinated axon.
The conduction of an action potential along a myelinated axon.
The conduction of an action potential along a demyelinated axon.
B
The resting potential for a particular neuron is measured to be -60 mV. Which of the following distributions of ions could not produce this measurement?
Please choose from one of the following options.
More cations than anions on both sides of the cell membrane
More anions than cations on the outside of the membrane, more cations than anions on the inside of the membrane
More cations than anions on the outside of the membrane, more anions than
cations on the inside of the membrane
More anions than cations on both sides of the cell membrane
A
In the resting state, which of the following mineral ions is found in greatest concentration inside a neuron?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Potassium cation
Chloride anion
Calcium cation
Sodium cation
A
In the resting state, which of the following mineral ions has an electrical force vector pointing out of the neuron?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Chloride anion
Calcium cation
Sodium cation
Potassium cation
D
Researchers use genetic engineering techniques to culture neuronal cells with sodium-potassium pumps that, for each molecule of ATP, transport 2 sodium cations for every 3 potassium cations; assuming that all other aspects are held equal, which of the following would be most affected by this change, as compared to what happens in a normal neuronal cell?
Please choose from one of the following options.
The diffusion force on potassium cations would be smaller and in the opposite direction
The diffusion force on potassium cations would be larger and in the opposite direction
The diffusion force on potassium cations would be smaller and in the same direction
The diffusion force on potassium cations would be larger and in the same direction
D
What is the primary difference in graded potentials versus actions potentials?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Graded potentials do not involve transient production of charged molecules inside the neuron, while action potentials involve the flow of charged molecules across the neuron membrane
Graded potentials occur in axons, while action potentials occur in the dendrites and soma
Graded potentials occur in neurons of the peripheral nervous system, while actions potentials occur in neurons of the central nervous system
Action potentials occur in axons, while graded potentials occur in the dendrites and soma
D
Nematodes are small worm-like animals with roughly 300 neurons. Imagine that a mutation is introduced into a population of nematodes that down-regulates the production of Schwann cells. Which of the following phenotypes would you predict to have a selective advantage in the population?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Nematodes with larger soma
Nematodes with smaller diameter axons
Nematodes with longer axons
Nematodes with shorter axons
C
Where are voltage-gated sodium channels found in greatest concentration?
Please choose from one of the following options.
In the axon terminals
In the nodes of Ranvier
In the trigger zones
In the dendrites
B
Reduced permeability of potassium leak channels would affect which of the following aspects of action potentials in a neuron?
Please choose from one of the following options.
The activation threshold
The time to reach maximum repolarization
The time to reach maximum depolarization
The size of the depolarization wave
A
Which of the following neurons is least likely to exist in nature?
Please choose from one of the following options.
A neuron that fires action potentials to a certain maximum amplitude, and increases this amplitude when it receives excitatory inputs
A neuron that fires action potentials at a steady state, and decreases this rate when it receives inhibitory inputs
A neuron that does not fire action potentials until stimulated by an excitatory input
A neuron that fires action potentials at a steady rate, and increases this rate when it receives excitatory inputs
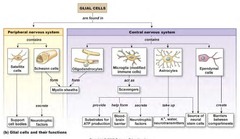
* Neurons
* Glial cells
Neural cells
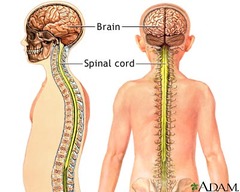
* Brain
* Spinal Cord
CNS
Neural tube=CNS
Neural Crest=PNS
neuro tube vs. neuro crest
glial cells (support cells)
Neurons ( send message)
some has nucleus
* some axons short others longer
* Some axons has more branches than others.
Look careful
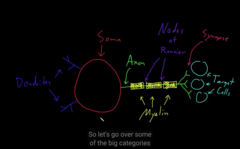
large axons gets covered by myeline,
take a careful look at the image!
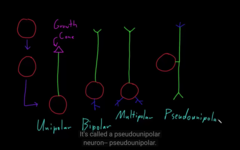
The neurons stem cells–> neuroblast–>unipolar
neuron.
“Types of neurons”
* Unipolar neuron
* Bipolar Neuron
* Multipolar Neuron (in adult)
* Pseudo unipolar Neuron
process and transmit information.
summation of all neurons gets added at the
axon hillock.
what are the function of neurons:
summation of the excitatory and inhibitory neurons as graded potential. AP is conducted the entire length of an axon, no matter how long it is
NT bind to the receptors on the target cells:
central summation turned into temporal summation
what are the function type of neurons
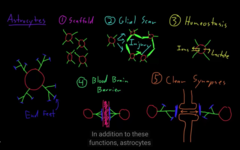
to protect the cells, they are end feet at the end of astrocyte processes
1) Astrocytes form scaffold
if injury in the brain or spinal cord, it will try to cover the cavity, they grow longer processes from a longer tissue. Scaffolding the CNS and structural support for the injury and the cavity.
2) Astrocytes scar
releases lactate and neurons little nutrient depends on the oxygen and glucose, neurons uses lactate if no glucose or oxygen.
3) Astrocytes Homeostasis
Astrocytes prevents molecules to pass from the into the blood vessel to the entering the brain.
4) Astrocytes Blood Brain Barrier
synapse connection, btw neurons and clearing the molecule communication. Astrocytes hard working cells of CNS.
5) Astrocytes clear synapse
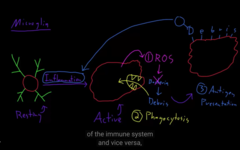
1) Reactive O species kill cell like bacteria
2) phagocytosis
the microglial cells acts like an immune system in the CNS, they find inflammation, it gets activated, and it kills the bacteria or whatever causing the inflammation.
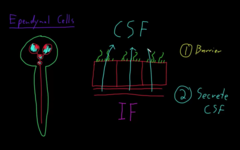
*simple epithelial cuboidal cells
* capillaries
IF=fluid between cells
* cilli and microvilli
The central fluid is called the central spinal fluid. The ependymal cells are covering the cells,
1) Barrier between cells form
2) Participate in secreting CSF
what are the two things formed by the ependymal cells?
It can militant multiple axons, myelin made of lipid, fat. Rubber coating insulation.
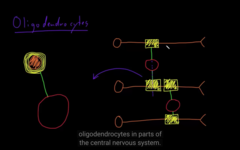
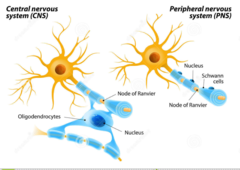
Oligodendrocytes
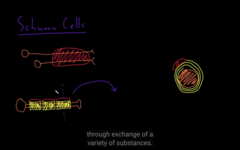
they only militate a single segment of the axon, provides support for the peripheral cells
glial of the PNS, schwan cells (shapeless cells)
oligodendrocytes vs. schwan cells
D
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Which part of the cell does it interact with?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Myelin sheath
Soma
Axon
Dendrites
C
Guillain-Barre syndrome is an autoimmune disease which attack gangliosides, which are molecules found on the outside of a cell. Patients with this disease have a nerve conduction block which is often caused by a slowed conduction potential and can lead to paralysis. Which type of cell is attacked?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Schwann cells
Neurons
C
What is the most common cell type in the brain?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Oligodendrocyte
Ependymal cell
Astrocyte
Neuron
C
The choroid plexus is a structure made of capillaries and modified neural cells that produces the fluid that cushions the central nervous system. What types of cells are found in the choroid plexus?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Oligodendrocytes
Neurons
Ependymal cells
Astrocytes
D
The microglia arise from which embryonic layer?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Neural crest
Mesoderm
D
A increased number of microglia would indicate which of the following?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Multiple sclerosis
Subdural hematoma
Peripheral nerve damage
Bacterial meningitis
A
The dorsal root ganglion (DRG) lies just outside the interface between the central and peripheral nervous systems, and holds the cell bodies for those neurons that transmit signals between the two. What type of neurons are found in the dorsal root ganglion?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Pseudounipolar
Monopolar
Multipolar
Bipolar
B
Which of the following is not a function of astrocytes?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Structural support
Interstitial fluid monitoring for pathogens
Barrier protection
Hypoxia buffering
C
A local nerve block is a technique which shuts off afferent receptors in the target area. What is its effect?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Temporary paralysis
Slows heart rate
Anesthetic
Anti-tetanus
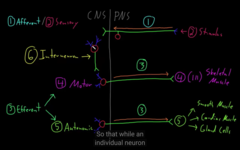
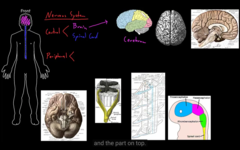
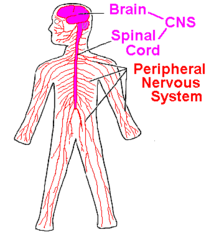
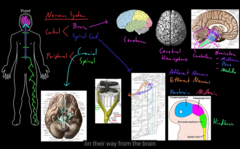
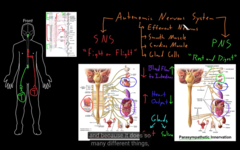
central=brain and spinal cord
peripheral=the rest.
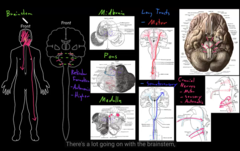
The structure of the Nervous System (central and peripheral)
* top: med brain
* middle: ponds
* bottom: medulla
brain stem
Prosencephalon: it cerebrem
forebrain
Mesencephalon : midbrain
Midbrain
Rhambincephalon : pons, medulla and cerebellum
Hindbrain
1) nerves carry axons of neurons
2) ganglia ( lumps attached to the nerve they contain the somas of the neurons)
PNS contains two types of structures
Afferent neurons —carry info into the CNS
Efferent neurons-carry info out into the PNS
There are a lot of nerves going all over the body
PNS information carries
comes out of the brain
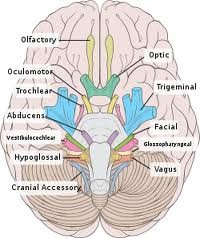
Cranial nerves
12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 spinal nerves
afferent and efferent, all nerves keep branching, proximal part of nerves: they branch and eventually becomes microscopic.
mix nerves
cranial nerves pass the skull out in the periphery
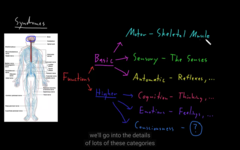
patterns of abnormal function.
Syndromes are what?
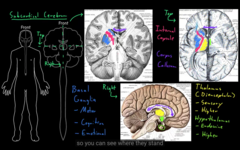
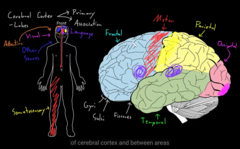
1) Basic Functions (made of CNS+ PNS)
2) Higher Functions
functions of the nervous system is divided into two sections:
the cranial nerves perform the basic function of cranial nerves while the spinal cord performs the function of the spinal region
basic function
1) Motor (skeletal muscle control) provides movement, posture and tone. End result of contraction
2) Sensory functions: anything that the nervous system can detect. (vision, hearing, smell, teste, vestibular sense, somato sensation)
3) Automatic no concious involvement, reflex is an example. control of body system
Basic functions of the CNS divided into 3 sections:
cognition: (thinking, learning, memory, language, executive)
emotions: feelings, experiance of life
consciousness: awareness of being a person and controlling ones action.
Higher part of the function is performed by parts of the brain: 3 categories,
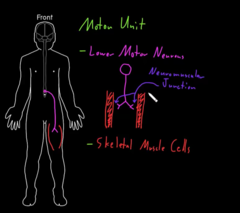
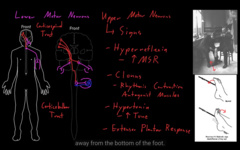
LMN (efferent) carrying information away from the CNS
control the skeletal muscles
—motor unit: one lower motor unit
—this motor neurons contacting two skeletal muscle cells, they are the other part of the motor unit.
The motor unit made of couple parts:
because when it contracts it causes all of the unit in the skeletal muscle to contract: the space b/w the muscle cells and the LMN is called a neuromuscular junction. All the cells are activated at the same time.
why it is called a motor unit?
the brain and spinal cord (skeletal muscles)
The lower motor neurons in the cranial controls
controls everywhere else. These muscles has small motor units, they are synapsing on the small muscles. Big muscles in the thigh, they have large motor units.
The motor unit of the spinal cord
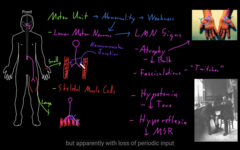
1) weakness, loss of contraction of skeletal muscle.
what happens if any kind of abnormality in the motor unit?
1) weakness and LMN signs,
Atrophy of skeletal muscle-decreases bulk of skeletal muscle, size is decreased. Thee muscles shrivel up
2) Fasciculation’s: twitch of skeletal muscle, involuntary, little twitch of the muscle happens. Lots of twitching happening
3) Hypotonia: a decreases in the tone of skeletal muscle, it refers to how muscle contracting, not as much tone.
3) Hyporeflexia=decrease muscle stretch reflexes, reflex happens if you rapidly strech.
Abnormality in the LMN
it provides problems in the areas of the body
If the LMN doesn’t provide constant stimulation to the skeletal muscle then the
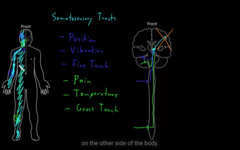
senses of the body,
* postion sense ( moving arm, you know it)
* vibration sense (turning fork)
* touch
* Pain
* temperature
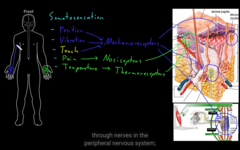
what are somatosensation
respond to physical forces: mechanoreceptors
* postion
* vibration
* Touch
what are some of the somatosensory receptors?
* postion
* vibration
* Touch
nociceptors
1) experiance of pain
What are some of the somator receptors for pain?
Thermoreceptors
what are some of the somatorsensory receptors of temp?
In the skin, there are number of axons entering the skins, mechanoreceptors: they tend to have structure on the end of the axon, close to the surface of the skin.
You can also find them in the deep tissue, they magnify one large in muscle. Relative position and body parts.
where these somatosensory receptors mostly found?
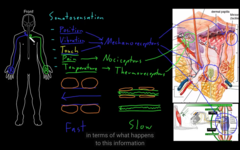
Temperature and pain moves slow
Position, vibration, Touch moves fast
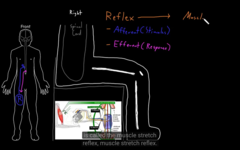
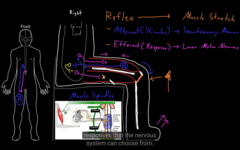
Reflex response to a stimulus that doesn’t require a point of consciousness
Reflex =afferent part (bring information about stimulus into the CNS)
Efferent=carries information away from the CNS causes response to a periphery.
Muscle stretch reflex: the nervous system forms many kind of reflexes
if a skeletal muscle is rapidly contracting, as a protective response from being stretched rapidly.
One of the good reflexes is called the muscle stretch reflex
the doc is heating in the tendon, hooks the muscle and bone, the renden stretches the large group of muscle, it stretches it and rapidly this happens, muscle stretch happens, it spread out. Muscle spindles, special fiber, neuron axon. stretch the fibers to bring it back to the CNS
Leg kick out to the stimulus the rubber hammer
Everything you must know about reflexes
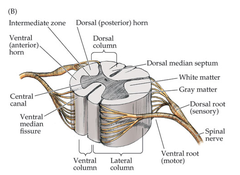
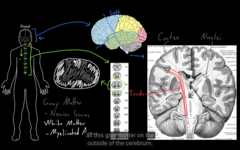
Gray matter vs. white matter
Everything you need to know on UMP
One side gets injured effects the other side of the body
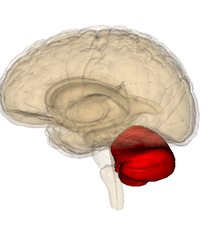
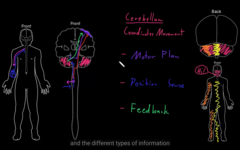
Cerebellum coordinating movement
lession studyies and exeprimental ablation
Lession studies and experimetal
It doesn’t tell us what areas of the brain is active at a given time.
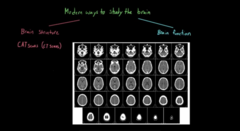
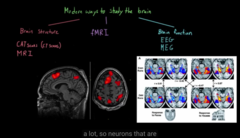
Different way to see the structure of a Brain
1) CT scan
uses radio waves and atoms of the brain line up, disturbs the atoms of the brains , can’t tell us the brain function
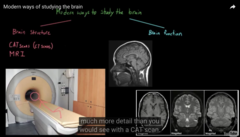
Different way to see the structure of a Brain
1) MRI
it gives wave lines, tells is person is awake or sleep.
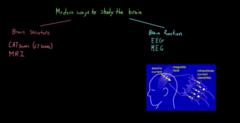
Different ways to see the function of the brain
EEG
requires more for room set up,
Different ways to see the function of the brain
MEG
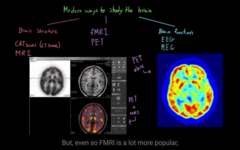
Different ways to see the structure/function of the brain
FMRI
inject brain with glucose to see the structures better.
Different ways to see the structure/function of the brain
PSCAN
D
Which of the following structures is a part of the rhombencephalon?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Temporal lobe
Thalamus
Substantia nigra
Medulla
D
Which of the following accurately describes the direction of an impulse moving through a neuron that carries information to the central nervous system (CNS) from the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Please choose from one of the following options.
An efferent neuron, impulse moving distally.
An afferent neuron, impulse moving distally.
An efferent neuron, impulse moving proximally.
An afferent neuron, impulse moving proximally.
C
Which of the following is an example of a basic nervous system function?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Learning English as a second language
Feeling afraid of the dark
Sweating during a yoga class
Remembering a painful experience
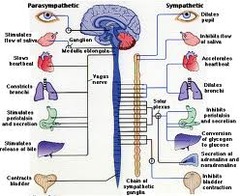
Sympathetic nervous system activation constricts arteries found within the salivary glands.
Which of the following statements correctly describes the activation of autonomic nervous system function within the circulatory system?
B
A 55-year old woman is diagnosed with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and reports symptoms of general weakness, muscle atrophy, and muscle twitching. What type of nervous system dysfunction is she likely experiencing?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Upper motor neuron dysfunction
Lower motor neuron dysfunction
Axon degeneration
Demyelination
C
If an individual were to sustain a significant injury to their right cerebral hemisphere, where might somatosensory loss of functioning occur?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Both sides of the body
Right side of the body
Left side of the body
There is no evidence that loss of functioning would occur.
C
A veteran is admitted to the hospital after sustaining a traumatic brain injury. A magnetic resonance image (MRI) shows significant damage to the veteran’s cerebellum. The damage would result in difficulty with which of the following functions?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Sensation of pain
Regulation of temperature
Coordination of movement
Regulation of emotion
D
A researcher is interested in learning more about individual perceptions of pain and develops a trial where participants experience electric shocks. He applies a low grade electric shock to a participant’s right hand. Where would this information typically be processed by the participant’s brain?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Pain sensation is not processed by cerebral cortex
Both sides of the cerebral cortex
Right side of the cerebral cortex
Left side of the cerebral cortex
B
Which of the following areas of the brain is not involved in the diffuse cortical projection of dopamine?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Hypothalamus
Raphe nuclei
Substantia nigra
Ventral tegmentum
D
Jenny receives a golden retriever puppy for her birthday. She picks up the puppy and is surprised at how soft and fluffy the puppy’s fur feels. What lobe of Jenny’s cerebral cortex first processes the information about the feel of the puppy’s fur?
Please choose from one of the following options.
Temporal lobe
Occipital lobe
Frontal lobe
Parietal lobe